Analysis of The Working Mechanism of Two Plate Molds in Injection Molding
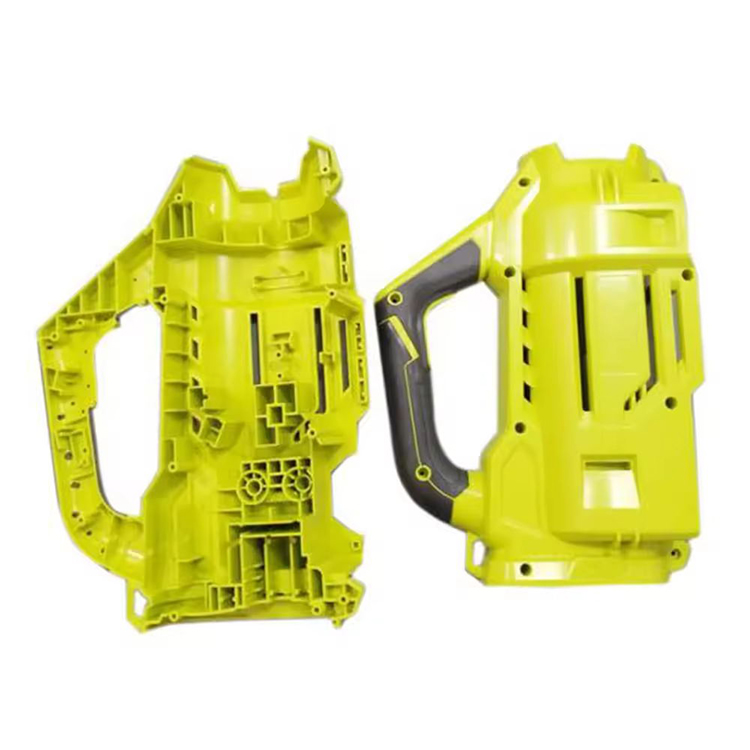
Two plate molds, as the mainstream type of molds in the field of injection molding, are widely used in the manufacturing of plastic cups, electronic product casings, automotive parts, and other products due to their simple structure and efficient production. The working process can be divided into four core stages, each of which requires precise control to ensure the quality of the plastic parts.
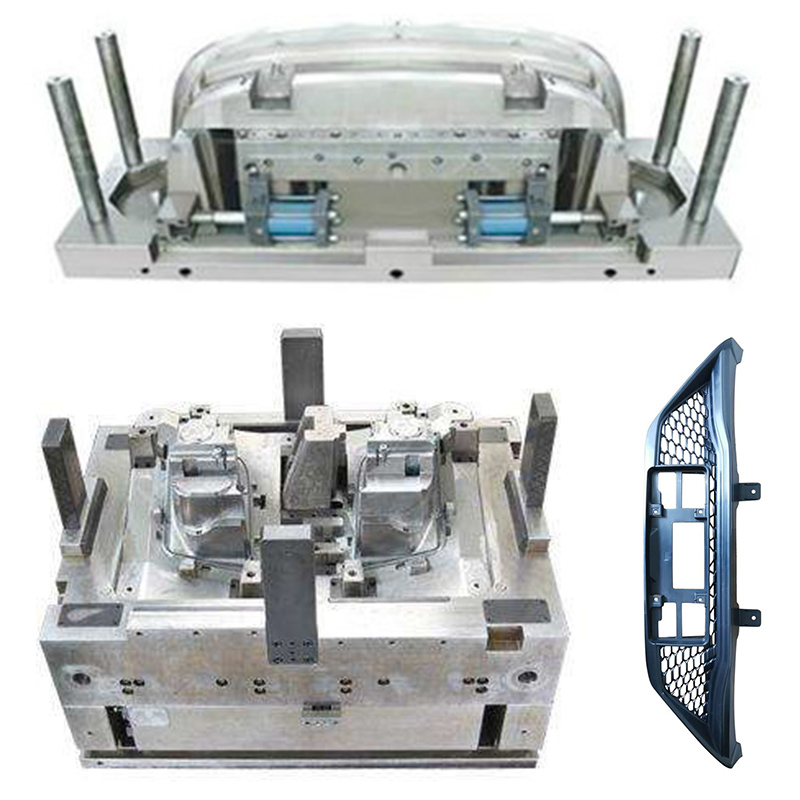
Structural composition
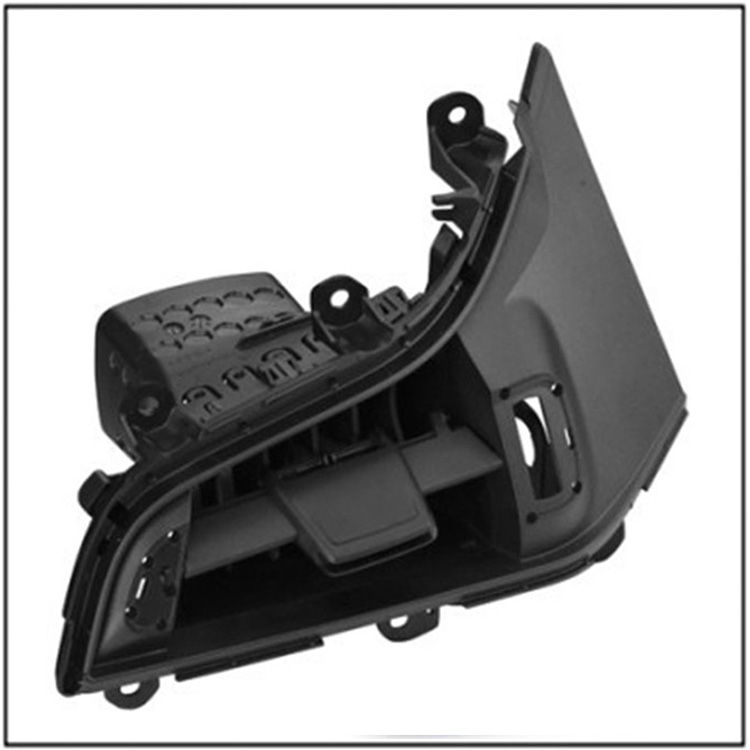
The two plate mold consists of two main parts: a fixed mold and a moving mold. The fixed part is fixed to the fixed plate of the injection molding machine, including components such as the mold cavity and the main channel liner; The moving mold is installed on the moving template and is equipped with structures such as a core and a top needle plate. When the mold is closed, the mating surface between the fixed mold and the moving mold forms a closed cavity, providing molding space for the plastic melt.
workflow
1.Mold closing stage
The moving mold rapidly moves towards the fixed mold under the drive of the injection molding machine until the parting surface is completely in contact. At this point, it is necessary to ensure accurate positioning of the guide column and guide sleeve to avoid mold deviation that may cause burrs or damage to the mold cavity. The clamping force is usually set at 100-150MPa to resist the melt pressure during the injection stage.
2.Injection filling
Molten plastic (temperature 180-250 ℃) is injected into the mold through an injection molding machine screw at a speed of 50-150mm/s. The size design of the sprue, as a channel for the molten material to enter the mold cavity, directly affects the filling effect. For example, a 0.8mm diameter sprue can complete the filling of the phone case cavity within 0.2 seconds, ensuring minimal weld lines.
3.Pressure holding cooling
After injection, the screw maintains a certain pressure (usually 60-80% of the injection pressure) to compensate for plastic cooling shrinkage. At the same time, the circulating water system inside the mold (with a water temperature of 20-50 ℃) is designed with a spiral waterway to cool the plastic parts to the ejection temperature (usually 30 ℃ lower than the hot deformation temperature). After optimizing the water circuit, the cooling time of a certain car lampshade mold was reduced from 25 seconds to 18 seconds.
4.Mold opening and demolding
When the moving mold is retracted and opened, the ejector pin system pushes the plastic part out of the mold cavity under hydraulic or mechanical drive. The distribution of top pins should be uniform, for example, on a 150mm × 100mm flat plastic part, 2-3 top pins should be arranged for every 1000mm ² area to avoid white top phenomenon. Gas assisted demolding technology can further improve the success rate of demolding.